Tooth pitch
- The tooth pitch corresponds to the number of teeth per inch (tpi = tooth per inch). One inch = 25.4 mm.
- The decisive factor for the correct choice of tooth pitch is the length of the blade engagement in the cut (cutting length).
- The quality of the material and the type of band saw blade chosen also play a role.
- A distinction is made between constant pitch with uniform tooth spacing and variable pitch with varying tooth spacing within the interval.
- Variable tooth pitch, e.g. 2-3 tpi, is characterized by two dimensions, where the lower number 2 is the minimum and the higher number 3 is the maximum pitch in a given interval.

Constant pitch with equal tooth spacing
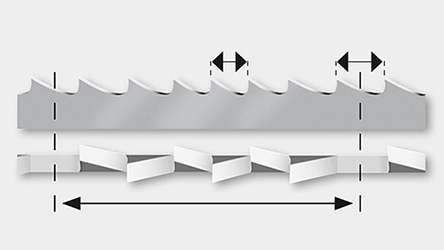
Variable pitch with variable tooth spacing
Tooth geometry
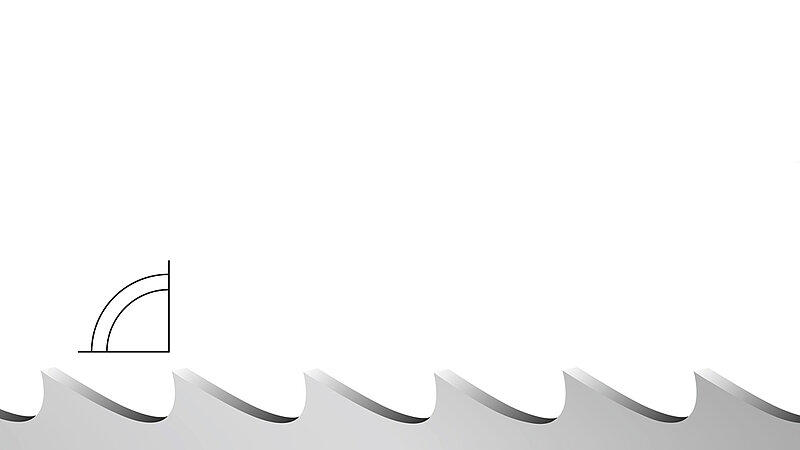

Standard (S)
Rake angle: 0°
- short chip-forming materials
- high carbon steels
- tool steel, cast iron
- workpieces with small cross-sections
- thin-walled profiles
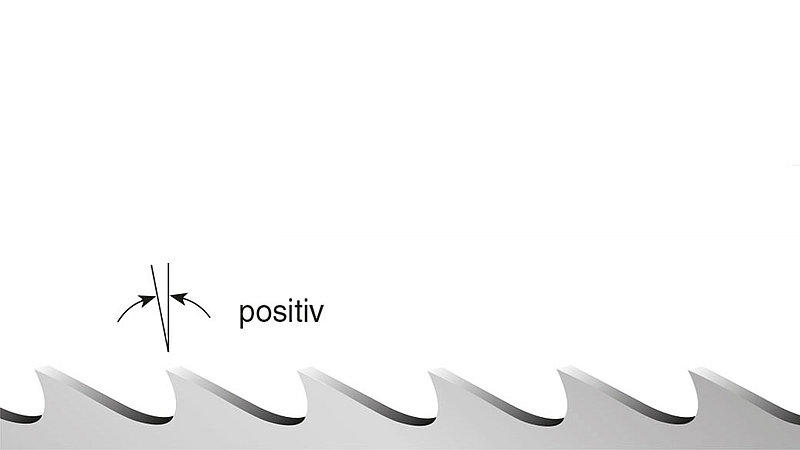
Positive (K)
Rake angle: positive 10-13°
- universal use
- steels and non-ferrous metals
- solid materials and thick-walled profiles

Extremely positive (K)
Rake angle: positive 15°
- difficult to cut materials
- stainless and acid-resistant steels and alloys (austenitic)
- duplex and heat-resistant steels
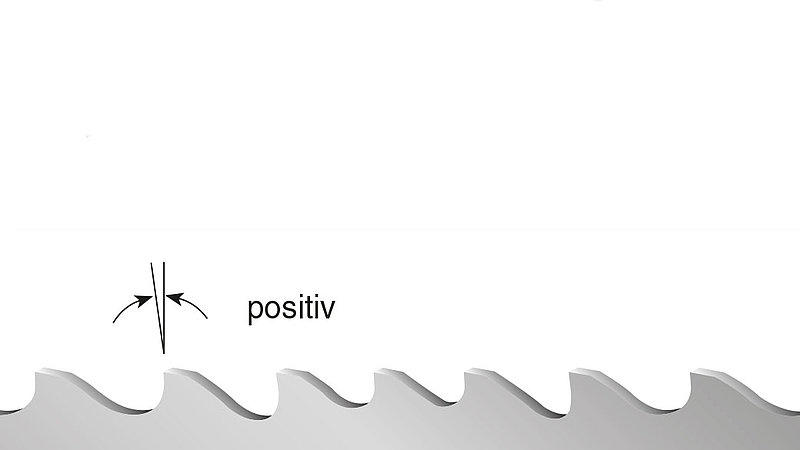

Profile (P)
Rake angle: positive 5-7°
- hollow profiles and angles
- cutting in bundles and layers
- wherever vibrations occur
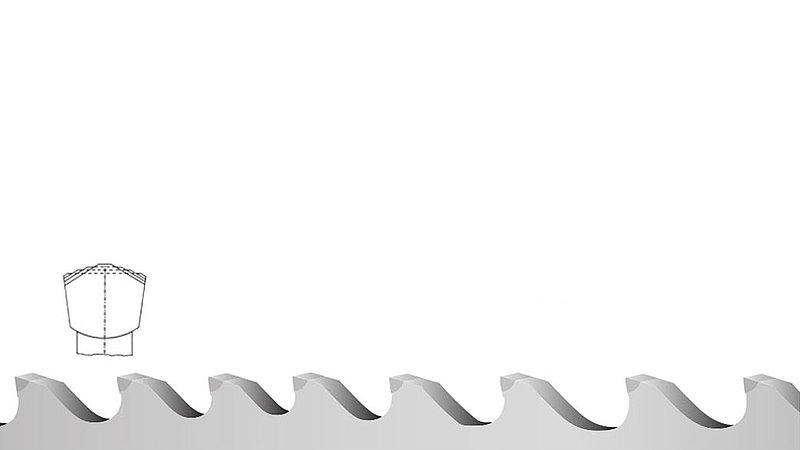
Trapezoid (T)
Rake angle: positive
- high cutting performance
- best surface quality
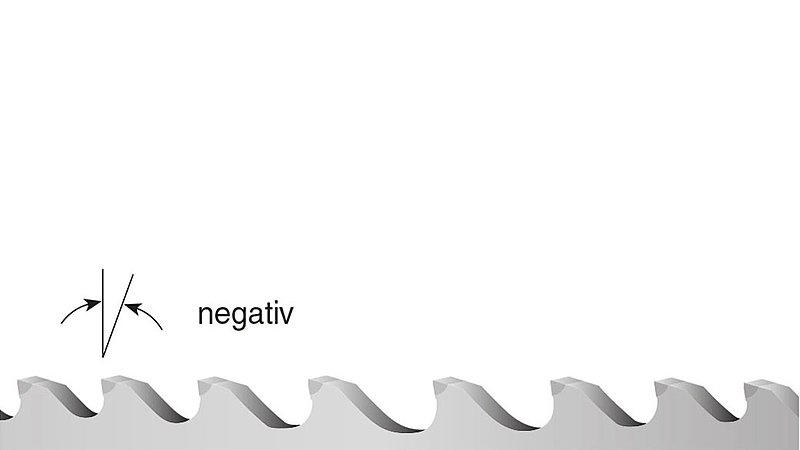
Trapezoid (TSN)
Rake angle: negative
- surface hardened shafts
- hardened steel up to 65 HRC, hard manganese steel, chrome-plated materials
- diameter up to 200 mm
Types of tooth setting
Free movement of the band saw blade in the cut is achieved by moving the teeth alternately left and right out of the plane of the blade body.
Standard setting (SD)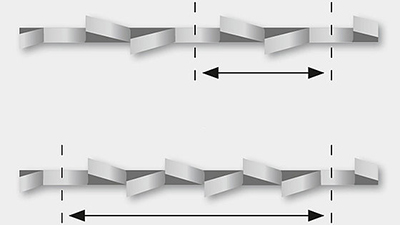
- Universally applicable for cutting steel, cast iron and hard non-ferrous metals with a thickness from 5 mm.
- Constant tooth pitch: left / right / straight adjustment sequence.
- Variable tooth pitch: at least one unset tooth in the interval, the remaining teeth are set repeatedly left / right or in reverse order.
Staggered setting (SFN)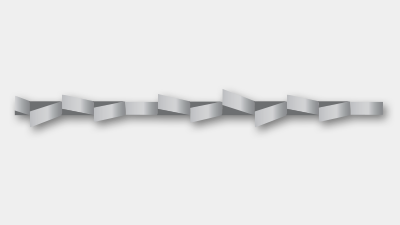
- Modified standard setting (SD).
- Variable tooth offset range and different tooth heights achieve a smoother saw blade cut, increased performance and longer service life.
Group setting (GS)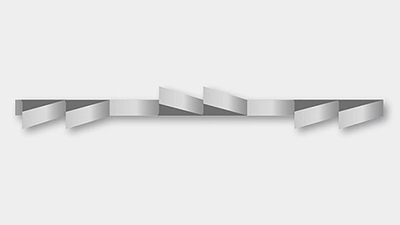
- Saw blades with a constant tooth pitch ranging from 4 to 18 tpi achieve a better quality of the cutting surface of the material to be cut when grouped.
Wavy setting (WS)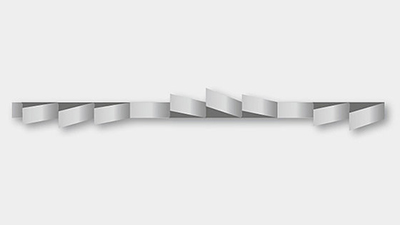
- For sheet metal, thin-walled tubes and profiles up to a material dimension of 5 mm.
Wide setting (SW / NE)
- Modified standard setting (SD).
- The teeth are more offset to prevent the band saw blade from jamming in the material.
- Typical application for structural steel beams with internal stress.
- Cutting of non-metallic materials (aluminium, bronze, etc.) and on machines with manual feeding.

Band saw blade selection
In order to design the right solution, we will need some basic information from you regarding the machine and the material to be cut. The machine will tell us the dimensions of the saw blade and the material will determine the direction to take.

Tooth pitch selection
The decisive factors for the choice of tooth pitch are the contact length of the blade in the workpiece (the longest uninterrupted part of the cut) and, in the case of profiles, the wall thickness. Choose the toothing suitable for your material.

